12 Common Daily Habits That Quietly Harm Your Health
Many of our daily routines are so ingrained that we rarely question their effects on our health. Yet, seemingly harmless habits can accumulate and negatively influence our well-being over time. From how we sit to the way we use our devices, subtle patterns may have long-term consequences. Recognizing these overlooked behaviors is the first step toward making positive changes.
By becoming more aware of these small actions, we can start to make intentional adjustments that support our overall health. Even minor improvements in posture or screen habits can lead to noticeable benefits. Over time, these conscious choices build a stronger foundation for long-term wellness.
1. Skipping Breakfast

Forgoing breakfast might seem harmless, but it can disrupt your metabolism, lower energy levels, and impair cognitive performance throughout the day. Research has shown that individuals who regularly skip breakfast are more likely to experience weight gain and have a higher risk of heart disease compared to daily breakfast eaters.
For example, a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that breakfast skippers had increased cholesterol levels and insulin resistance, highlighting the importance of a nutritious morning meal for optimal health.
2. Sitting for Extended Periods

Prolonged sitting, whether at a desk or in front of a screen, is associated with increased risks of obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and chronic back pain. According to the CDC, sedentary behavior can significantly raise the likelihood of serious health issues compared to more active lifestyles.
In contrast, people who incorporate regular movement into their day experience improved metabolism and lower disease rates. Simple changes, like standing breaks or short walks, can counteract the negative effects of excessive sitting and support long-term health.
3. Neglecting Hydration

Chronic dehydration often goes unnoticed but can have profound effects on your health, contributing to headaches, fatigue, poor concentration, and even kidney strain. Many individuals fail to consume adequate fluids throughout the day, which impacts both physical and mental performance.
The U.S. Geological Survey and CDC recommend aiming for about 8 cups of water daily, though individual needs may vary. Staying mindful of hydration supports everything from energy levels to organ function and overall well-being.
4. Excessive Screen Time

Spending long hours on phones, computers, or TVs can result in digital eye strain, disrupted sleep patterns, and increased risk of anxiety and depression. The American Academy of Ophthalmology warns that excessive screen use leads to symptoms like dry eyes and headaches.
Additionally, a Sleep Foundation study links screen time before bed to poorer sleep quality. Experts recommend regular breaks, limiting evening device use, and following the 20-20-20 rule to reduce negative impacts on eye health and mental well-being.
5. Poor Posture
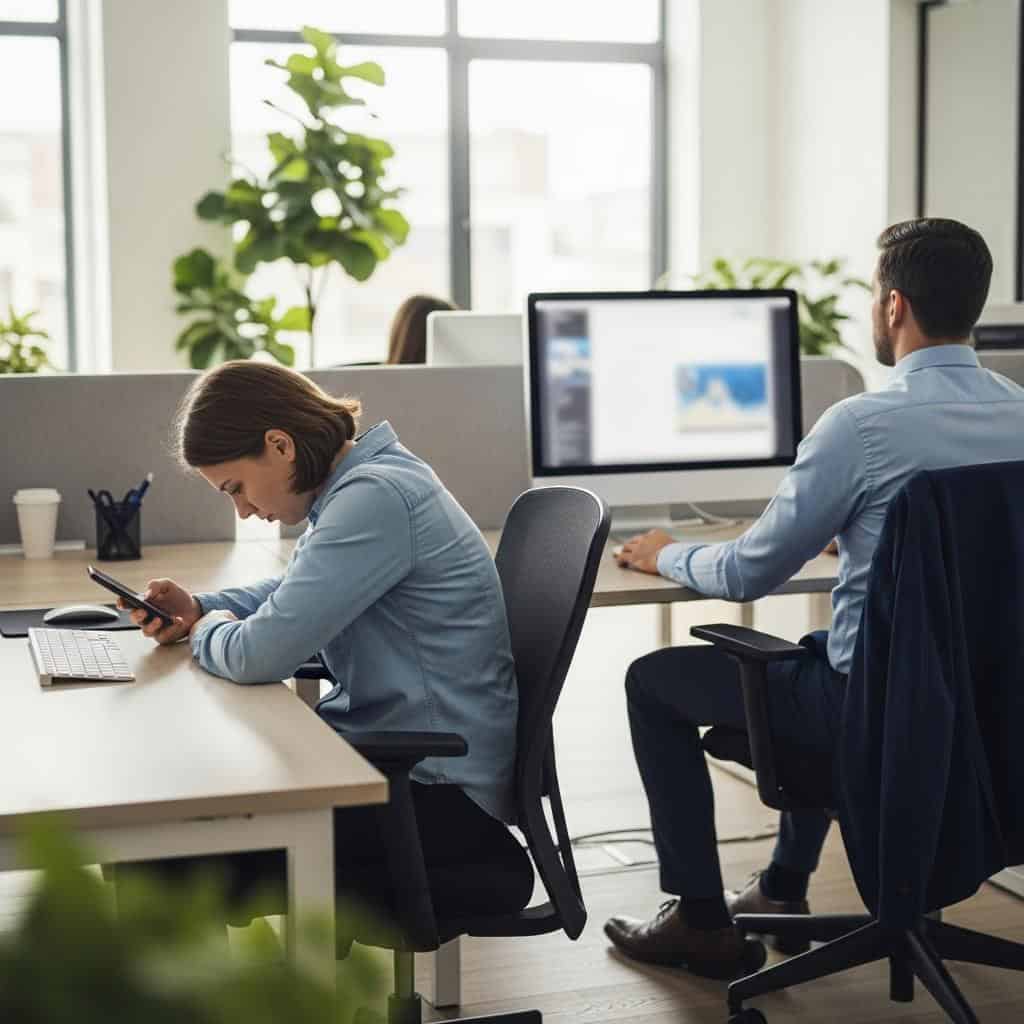

Slouching at your desk or hunching over a phone may seem harmless, but poor posture can lead to chronic back, neck, and shoulder pain, persistent fatigue, and even digestive issues by compressing abdominal organs. In contrast, good posture—such as sitting with shoulders relaxed and feet flat on the floor—supports spinal alignment and efficient body function.
The Cleveland Clinic highlights that maintaining proper posture not only eases musculoskeletal strain but also improves breathing and digestion, underscoring the value of staying mindful of body alignment in daily activities.
6. Not Getting Enough Sleep
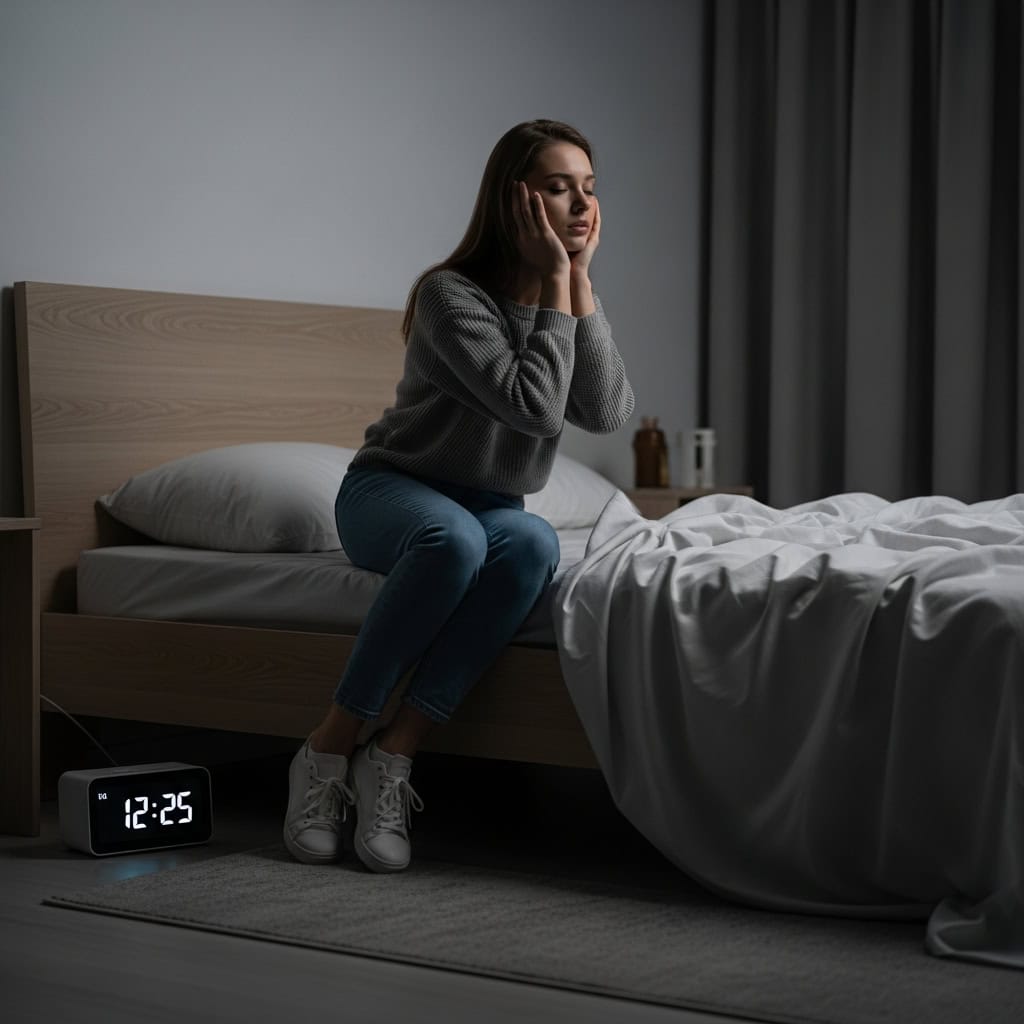

Regularly skimping on sleep can weaken your immune system, impair memory, and heighten your risk for accidents and chronic diseases. According to the CDC, adults should aim for at least seven hours of sleep per night to maintain optimal health.
Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to increased incidences of heart disease, diabetes, and mood disorders. Research from the Sleep Foundation emphasizes that quality sleep is essential for cognitive function, emotional regulation, and physical safety during daily tasks.
7. Overusing Headphones

Listening to music or podcasts at high volumes through headphones poses a significant risk of permanent hearing loss and increases the likelihood of ear infections. According to the CDC, sounds above 85 decibels can damage hearing over time, especially with prolonged exposure.
Safe listening practices include keeping the volume below 60% of the maximum and taking regular breaks. In contrast, consistently high volumes or using earbuds for hours without breaks can significantly raise the risk of auditory damage and inner ear discomfort, especially among young adults and teens.
8. Mindless Snacking

Unconscious snacking, especially while watching TV or working, can lead to consuming excess calories and eventual weight gain. Studies, such as those cited by Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, reveal that people often underestimate the quantity and quality of snacks eaten in distraction-filled environments.
Instead of reaching for chips or sweets out of habit, consider healthier alternatives like fresh fruit, nuts, or yogurt. Practicing mindful eating—paying attention to hunger cues and savoring each bite—can help reduce overeating and foster a healthier relationship with food.
9. Neglecting Dental Hygiene

Skipping regular brushing and flossing can lead to more than just cavities; it significantly increases the risk of gum disease, which has been linked to serious systemic issues like heart disease and diabetes. The CDC emphasizes the importance of twice-daily brushing, daily flossing, and routine dental checkups to prevent plaque buildup and infection.
Research has shown that poor oral health can contribute to inflammation throughout the body, making diligent dental care an essential part of overall well-being, not just for a bright smile but for long-term health.
10. Multitasking During Meals
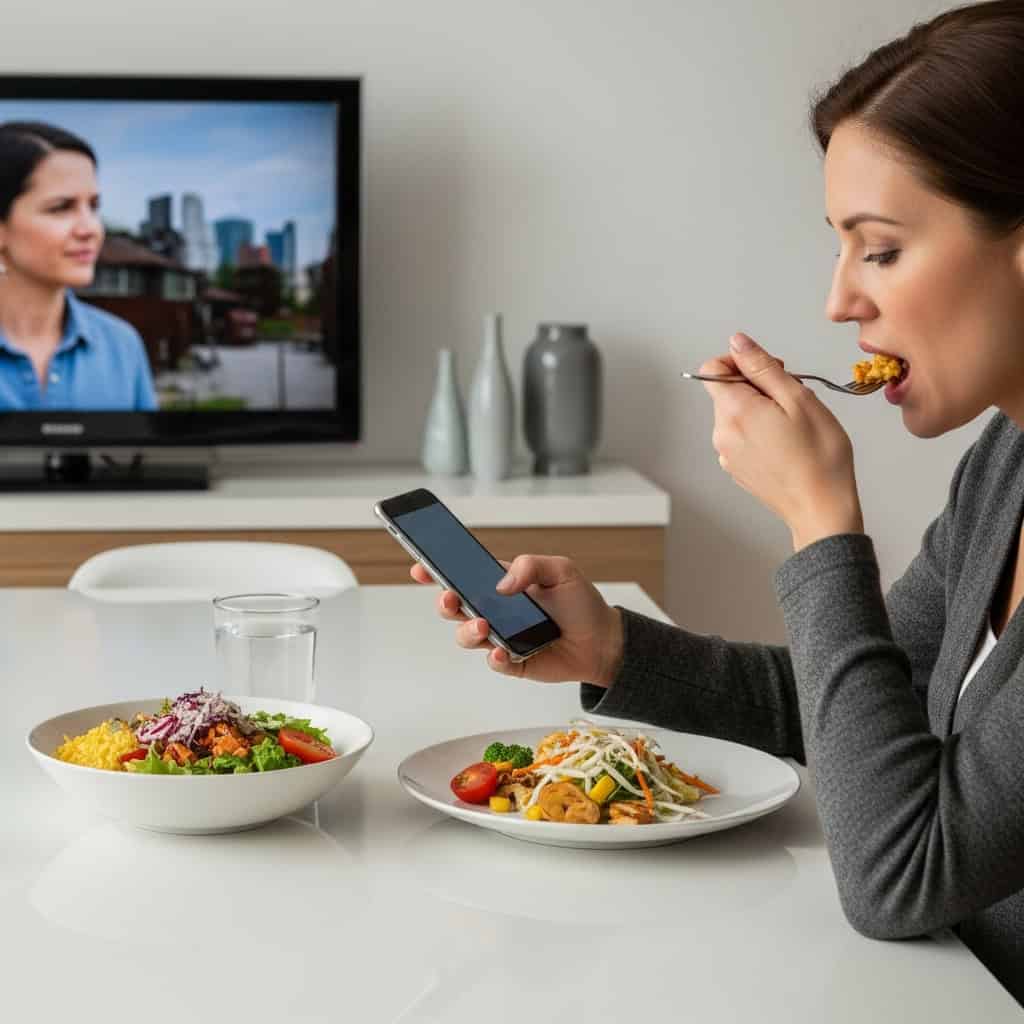

Eating while watching TV, working, or scrolling on your phone can lead to overeating and impaired digestion. Nutrition experts, such as those at the Harvard Health Blog, note that distracted eating makes it harder to recognize feelings of fullness, resulting in increased calorie intake.
Recent research suggests that multitasking during meals can also slow digestion and reduce satisfaction, prompting unhealthy snacking later. Making mealtimes device-free and focusing on the flavors and textures of your food can improve portion control, digestion, and your overall relationship with eating.
11. Ignoring Stress Management
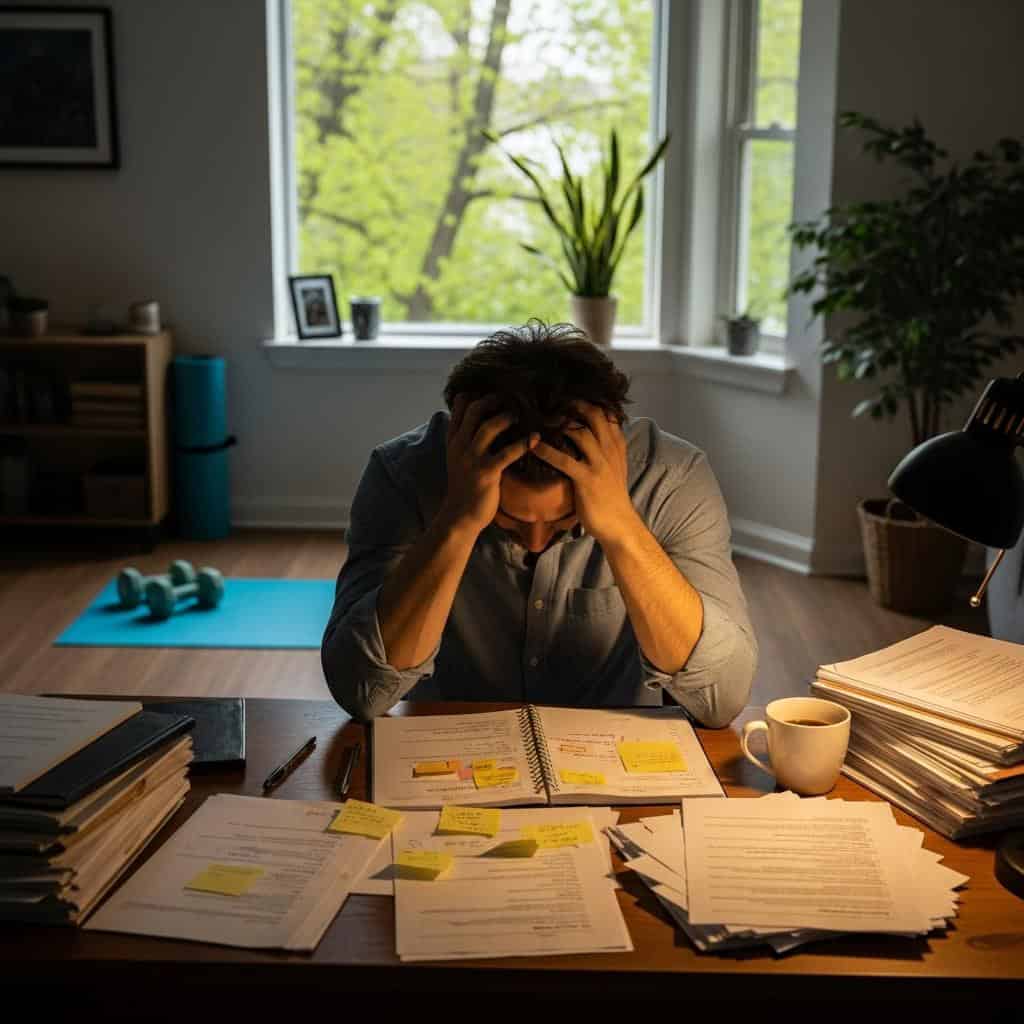

Chronic stress can quietly undermine your health, increasing the risk of heart disease, mood disorders, and weakened immunity. According to the American Psychological Association, unaddressed stress contributes to hypertension, anxiety, and frequent illness. Over time, ongoing tension drains energy and affects sleep quality.
Effective management techniques include daily physical activity, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness practices. The National Institute of Mental Health recommends setting boundaries, seeking social support, and taking short breaks throughout the day to help buffer the negative effects of stress on body and mind.
12. Using Smartphones Before Bed
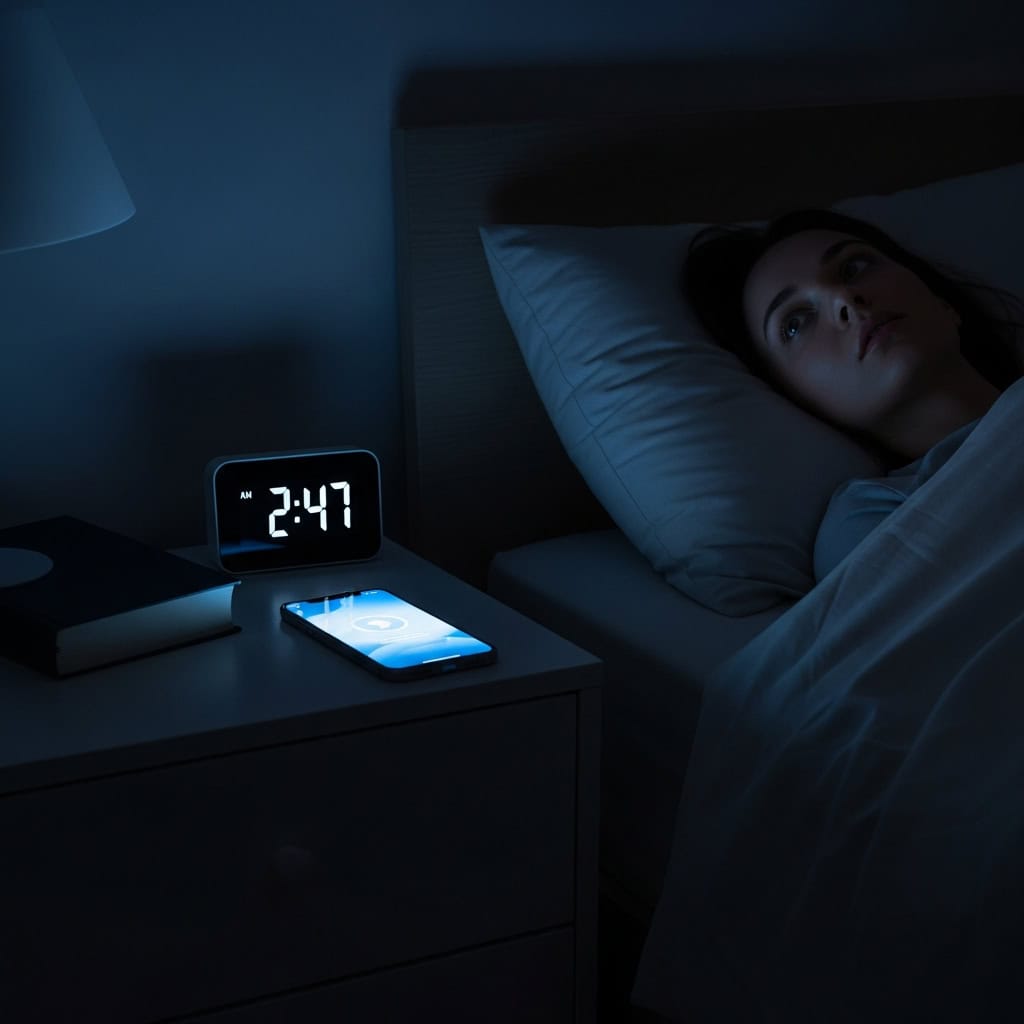

Scrolling through your smartphone before sleep can disrupt your circadian rhythm and reduce sleep quality. The blue light emitted by screens suppresses melatonin production, making it harder to fall and stay asleep, according to research from the Sleep Foundation. Poor sleep from bedtime device use has been linked to increased daytime fatigue and mood disturbances.
Experts recommend establishing a tech-free wind-down routine—such as reading a physical book, meditating, or gentle stretching—at least 30 minutes before bed to promote restful sleep and maintain a healthy body clock.
Conclusion & Disclaimer

Making small, mindful adjustments to everyday routines can have a lasting positive impact on your overall health. Addressing these common habits empowers you to protect your well-being and enjoy a higher quality of life over time.
Remember, individual health needs can vary widely—always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and recommendations. For more information on healthy lifestyle changes, visit resources like the CDC and World Health Organization.